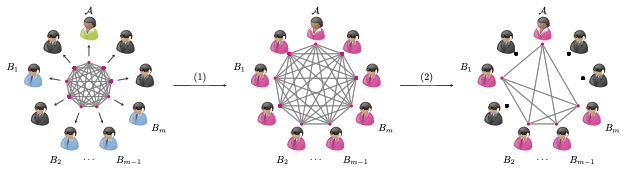
Anonymous communication
Anonymous communication conveys the idea that people may wish to send or receive information over a network, without having to reveal their identities. The clearest example of this is when this information is a message: ‘I would like to send “A” a message over the internet, but I don’t want anyone else to know that it was me who sends it, or “A” that received it’.
Usually, anonymity is considered in conjunction with secret communication, which hides the contents of the message itself. Secret communication is facilitated by encryption; anonymous and secret communication therefore needs anonymous encryption. The generalisation of this to more than one sender and one receiver is called anonymous conference key agreement (ACKA) - much of my research has explored ACKA, ranging from the first proof of concept to more mature protocols in various settings, as well as experimental implementations and showcases.
More recently, we have also considered anonymity in other networking tasks. More specifically, we have been exploring anonymous private parameter estimation, where a network of quantum sensors holding a parameter can establish their average, without having to give up any information about the individual parameters, nor the identities of the nodes in the network.
Overview of publications
An overview of my publications in the topic is as follows:
1. Anonymous Conference Key Agreement (arxiv, Published)
Hahn, de Jong, Pappa - Anonymous Conference Key Agreement. PRX Quantum 1, 020325 (2020).
- The first proof of concept for anonymous conference key agreement (ACKA) in quantum networks.
2. Anonymous and secret communications in quantum networks (arxiv, Published)
Thalacker, Hahn, de Jong, Pappa, Barz - New J. Phys. 23 083026 (2021).
- Experimental realization of the first ACKA protocol.
3. Secure Anonymous Conferencing in Quantum Networks (arxiv, Published)
Grasselli*, Murta*, de Jong, Hahn, Bruß, Kampermann, Pappa - PRX Quantum 3, 040306 (2022). * these authors have contributed equally.
- An improved ACKA protocol that is both robust and more secure. Includes finite key analysis and simulations.
4. Anonymous conference key agreement in linear quantum networks (arxiv, Published)
de Jong, Hahn, Eisert, Walk, Pappa - Quantum 7, 1117 (2023).
- An ACKA protocol that uses linear networks, which are much easier to realize than the central networks of the previous protocols.
5. Experimental ACKA using linear cluster states (arxiv, Published)
Rückle, Budde, de Jong, Hahn, Pappa, Barz - Phys. Rev. Research 5, 033222 (2023).
- Experimental realization of the ACKA protocol in linear networks.
8. Anonymous and private parameter estimation in networks of quantum sensors (arxiv, Published)
de Jong, Scheiner, Solomons, Chaoui, Markham, Pappa - Phys. Rev. Applied 24, 054053 (2025).
- The first network sensing protocol to perform parameter estimation in both a private and anonymous fashion.